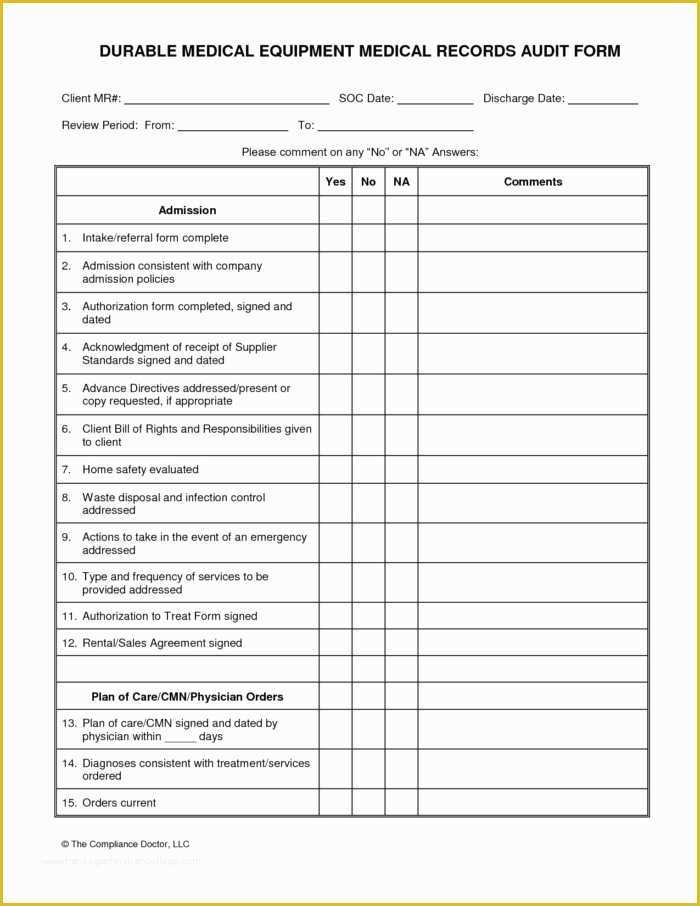
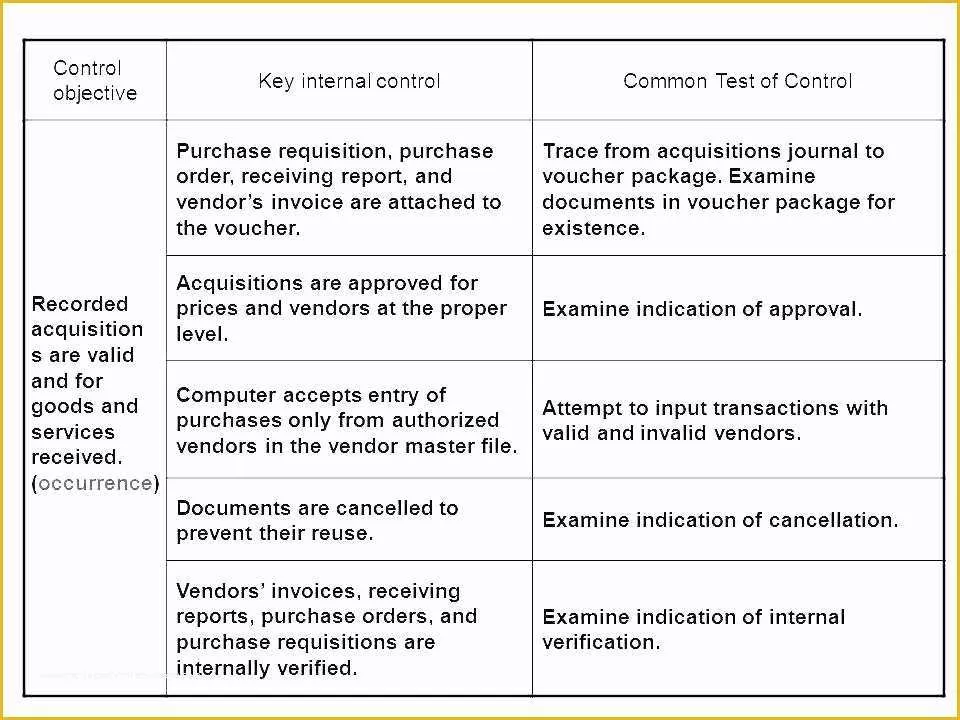
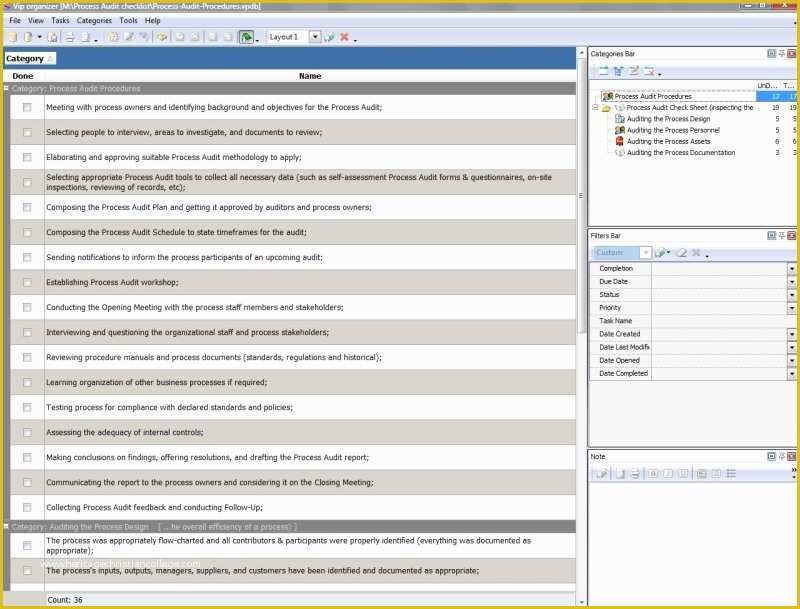
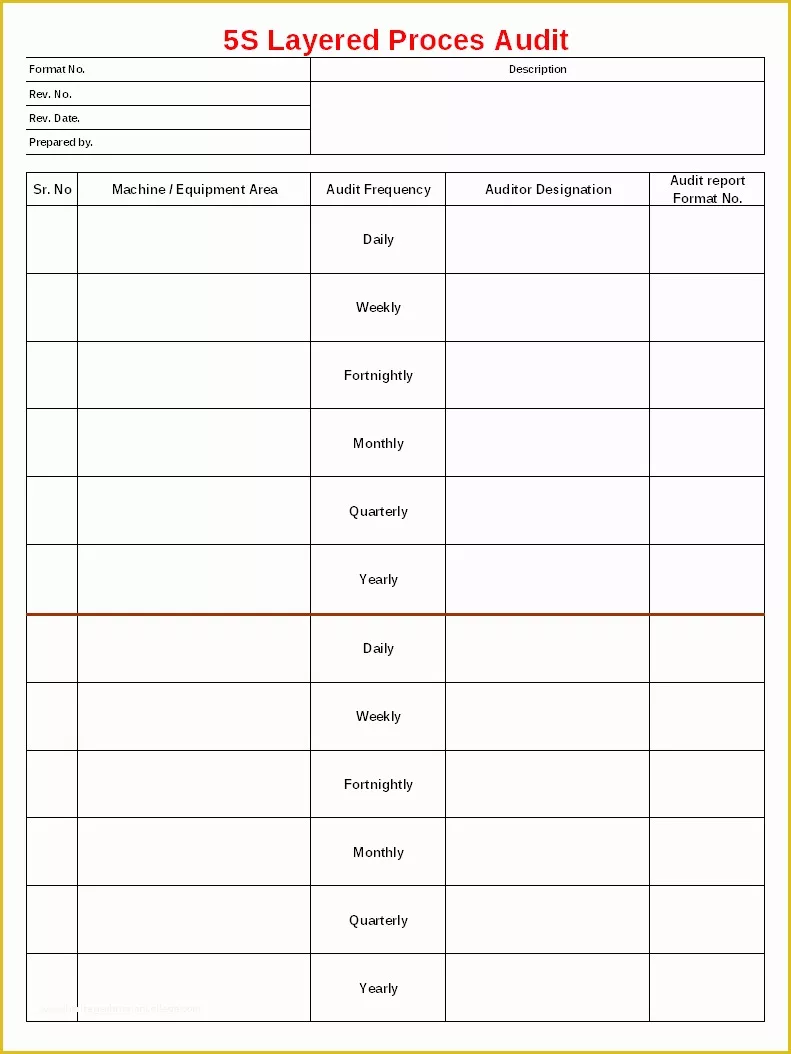
Layered Process Audit Example. Quite simply, Layered Process Audits (LPAs) are a process based approach to conducting internal audits. When imple-mented well, LPA will improve First Time Quality (FTC), reduce waste, improve throughput and curb costs.
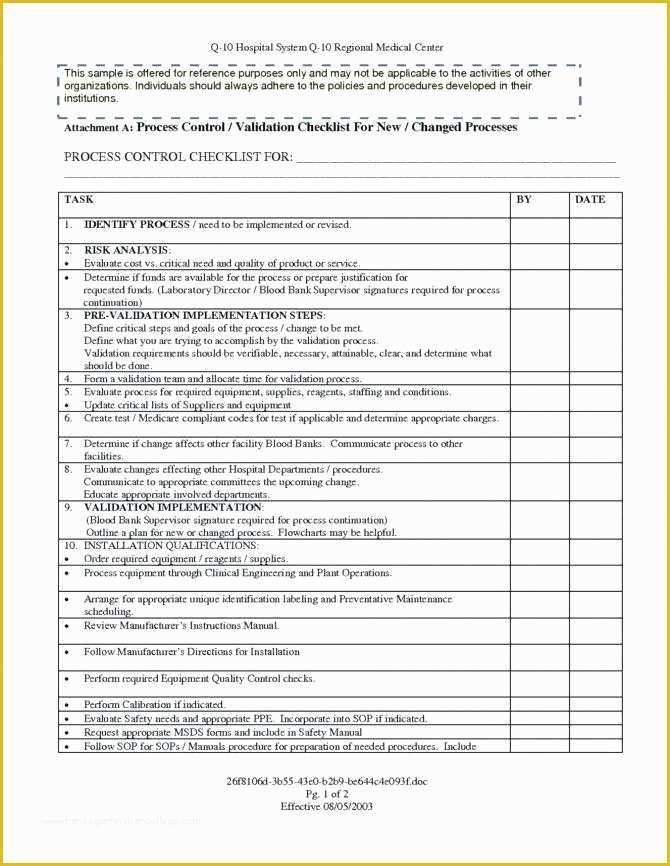
A process audit is an examination of results to determine whether the activities, resources and behaviours that cause them are being managed efficiently and effectively.
When utilized properly, LPA will drive cultural change throughout an organization to improve quality, reduce scrap and rework. - Concise: People who are not process experts should be able to easily answer the questions.
Managing Process Audit through Audit Planning, Audit Scheduling and Audit Audit Process: To begin with, audits are triggered-to-start ad hoc or based off of a pre-set schedule. With LPAs, every layer of management participates in daily checks of high-risk processes. Because there is no sanctioned process audit standard Is auditing a process by clause requirements or elements a process audit?